Valves
Introduction:
Valves are essential components of a piping system, and they allow the process fluid to be controlled and directed on its journey through the process plant. Valves can control not the flow, but also the rate, the volume, the pressure, and the direction of a fluid within a pipe.
The Function of a Valve:
- Isolation: on/off
- Regulation: throttle flow
- Non Return: Check, prevent flow reversal
- Pressure relief
Valve Classification:
i. Based on Mechanical Motion
Linear Motion Valve: In this valve closure member moves in a straight line to allow, stop, or throttle the flow. Examples are Gate, Globe, Diaphragm, Pinch, and Lift check valves.
Rotatory Motion Valve: In this valve closure member travels along an angular or circular path. Examples are Butterfly, Ball, Plug, Eccentric and Swing check valves.
Quarter Turn Valves: Some rotatory valves require approximately a quarter turn, 0 through 90° motion of the stem to go to fully open from a fully closed position or vice versa.
ii. Based on Operation:
Manual: Manual operators employ levers, gears, or wheels to facilitate movement within a valve.
Automatic: Automatic operators known as actuators use an external power supply to provide the necessary force required operate valves. Automatic actuators use hydraulic, pneumatic, or electrical power as their source for operating valves. Hydraulic and Pneumatic actuators use fluid or air pressure to operate valves needing linear or quarter turn movements. Electric actuators have motor drives that operate valves requiring multiple turn movements.
Dimensions needed when drawing a Valve:
- Face to Face - The lenght of a valve is represented as Face to Face Dimension.
- Handwheel height - Height from centerline of a valve to the stem tip.
- Handwheel diameter
- Diameter of the flanged faces on flanged valves.
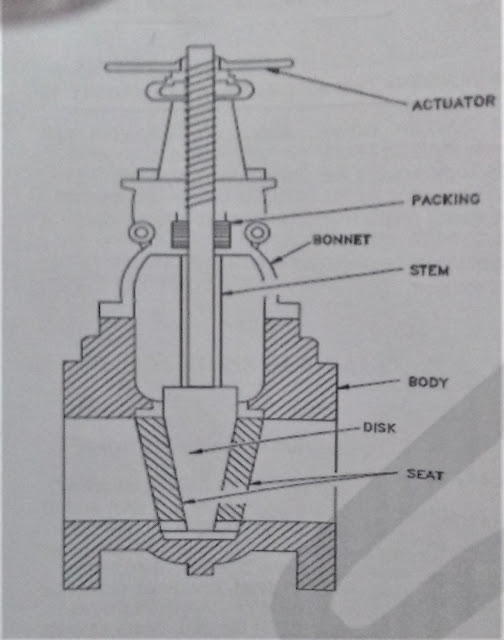
Valve Components:
The following are the primary components of a valve:
- A Valve body is the housing for all the internal working components of a valve and it contains the method of joining the valve to the piping system.
- The closure member known as the disk or plug, is a valve component that when moved, opens or closes to allow the passage of fluid through the valve. The mating surface of the disk bears against the seat.
- The Actuator is a movable component that when operated, causes the closure member element to open or close.
- The stem is a movable component that connects the actuator to the closure element.
- The Bonnet is a valve component that provides a leak proof closure for the body through which the stem passes and is sealed.
- The Seat is a component that provides a surface capable of sealing against the flow of fluids in a valve when contacted by a mating surface on the disk. The seat is attached to the valve body.
- The stuffing box is the interior area of the valve between the stem and the bonnet that contains packing.
- Packing is the material that seals the stem from leaking to the outside of the valve. The packing is contained by the packing nut on the bonnet.
- The Backseat is a seat in bonnet used in the fully open position to seal the valve stem against leakage into the packing.
- A bushing on the stem provides the mating surface.
- Backseating is useful if the packing begins to leak and it provides a means to prevent the stem from being ejected from the valve.
- The stroke of a closure member is the distance the member must travel from the fully opened to the fully closed position.
Two types of valve stems are Rising stems & Non Rising stems.
For Rising stem valve, the stem will rise above the actuator as the valve is opened. This occurs because the stem is threaded and mated with the bushing threads of a yoke that is an integral part to the bonnet.
There is no upward stem movement from outside the valve for a non rising stem design. For the non rising stem, Valve disk is threaded internally and mates with the stem threads.
Types of Valves:
Due to the various environments, system fluids and system conditions in which flow must be controlled, a large number of valve designs have been developed. The Valves are designed from ASME B31 code. The various valves are:

Comments
Post a Comment