Piping Materials
Introduction
There are many comprehensive list of materials used to manufacture pipe. Some of the materials include concrete, glass, lead, brass, copper, plastic, aluminium, cast iron, carbon steel, steel alloys.
Vital Characteristics Required in Material :
- Toughness
- Creep Strength
- Ductility
- Good Surface Finish
- Hardness
Factors Affecting Selection of Piping Materials :
- Mechanical Properties - Tensile, Yield, Creep, Rupture, Fatigue and Impact.
- Performance requirements and Material Reliability.
- Safety.
- Environment Conditions.
- Availability.
- Resistance to erosion and corrosion.
- Economic Factors.
Classification of Piping Materials
PVC - Polyvinylchloride | HDPE - High Density Poly Ethylene | LDPE - Low Density Poly EthylenePTFE - Polytetrafluoroethylene | FRP - Fibre Reinforced Plastics
Here we are only going to learn about common materials used in piping.
[I] Ferrous Materials
1) Carbon Steel :
- Carbon steel is an alloy of Carbon & Iron.
- It contains 0.1 to 1.5% C, Mn of 1.6%, Si of 0.6%, S of 0.1%, P of 0.1%.
- Carbon steel pipe is the most common material used in piping industry.
- Based on their carbon content,there are three groups Low Carbon Steel, Medium Carbon Steel, High Carbon Steel.
Mild Steel is the most commonly used ferrous metal. it exhibit
High tensile strength, Toughness & Ductility. it contains approximately 0.15 to 0.25% carbon.Because of the low carbon content it cannot be hardened and tempered.it must be casehardened.it used in manufacturing of plates, nuts, bolts etc.
(ii) Medium Carbon Steel
It has approximately 0.25 to 0.5% carbon content.it is stronger and harder than mild steels but has less ductility, toughness & malleability. it is used in making steel ropes, wire, garden tools, springs etc.
(iii) High Carbon Steel
It is a ferrous metal that has approximately 0.50% or more carbon. it is the hardest of the carbon steel but is less ductile, toughness, & malleable.
- Alloy steels are steel to which one or more alloying elements other than carbon are added to give them special properties.
- Commonly used alloying elements are Si, Cr, Ni, Mo, Mn, V, W, Ti, B, Al, Co.
3) Cast Iron :
- Cast iron is a group of Iron Carbon alloys with a carbon content more than 2% along with varying amounts of silicon and manganese and traces of impurities such as sulfur and phosphorus.
- Most cast iron is either so-called gray iron or white iron, the colours shown by fracture. Gray iron contains more silicon and is less hard and more machinable than is white iron.
- Cast iron is brittle and ease of machining, vibration dampening, compressive strength, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
- What makes Cast Iron different is that when it corrodes, an insoluble layer of graphite compounds is produced. the density and adherent strength of these compounds form a barrier around the pipe that prevents further corrosion.
- Cast iron is the least expensive material.
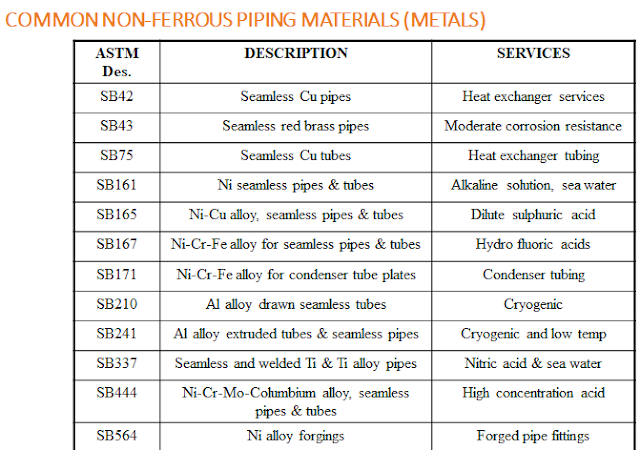
[II] Non Ferrous Materials
1) Copper & its Alloys :
- Used when heat and electrical conductivity are important.
- Thermal Conductivity is high.
- Alloys are Brasses, Bronze (Cu-Sn), and Cupronickel (Cu-Ni)
- Bronze display good strength with corrosion resistance.
- Cupronickel has the highest corrosion resistance among Cu alloys.It is used in heat exchanger tubing.
2) Nickel & its Alloys :
- Easy Machinability & Weldability.
- Chloromet & Hastelloy are widely used other than monel 400
- Not resistant to oxidising environments.
- Monel 400 is used to handle dilute sulphuric acid and hyrochloric acid.
- Alkalis and sea water do not affect Nickel.
3) Aluminium & and its Alloys :
- Good thermal conductivity & most workable metal.
- Highly resistant to atmospheric conditions, industrial fumes, fresh brackish or salt water.
- Not resistant to corrosion.
- Loses strength rapidly at 175 C.
4) Titanium :
- Strong and medium weight.
- Titanium oxide is formed prevents corrosion.
- Resistant to nitric acid of all concentration except fuming nitric acid.
- Provides good resistance to hydrochloric acid when alloyed with 30% molybdenum.
- Loses strength above 400 C.
- Not affected by impingement and crevice corrosion.
1) PVC Pipes :
- PVC, in full polyvinyl chloride, a synthetic resin made from the polymerization of vinyl chloride.
- No physical deterioration when exposed to direct sunlight
- Does not support combustion & no scales are formed inside the surface
- Extensively used in highly corrosive application involving acids, alkalis, salt solution, alcohol etc.
- used in gas transmission service & salt water disposal of oil fields.
2) Plastic Pipes :
- Plastic pipes has emerged as a reliable, safe, and cost effective alternative material.
- There are two categories Fluoroplastics & Thermoplastics.
- Fluroplastics are found in materials like PTFE, PVDF, ECTFE, CTFE, PFA & FEP.
- Fluroplastics perform extremely well in aggressive chemical services at -328 F to 500 F.
- Thermoplastics melt when heated and can be hardened when cooled.
- Thermoplastic are found in polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polycarbonate etc.
3) Concrete Pipes :

- Types - Reinforced & Non Reinforced.
- Some non reinforced material are ASTM C 14, AASHO M86, ASTM C412 etc. The pipe size can vary from 12" to 24".
- Some reinforced materials are ASTM C76, AASHO M170, SS-P-375 etc.
- Used for sewage and industrial waste, Strom waste, culverts, water supply.
4) Asbestos Cement Pipe :
- Not commonly used pipe.
- Some materials are ASTM C296, AWWA C400, SS-P-331, etc.
- Used for drains and industrial waste.
[IV] Lined Material :
1) Rubber Lined Pipes :
- Natural and Synthetic rubber linings are used to counteract corossion.
- Used in Temperature range of -20 C to 50 C.
- Commonly used natural rubbers are Soft, Semi hard, hard rubbers.
- Commonly used Synthetic rubbers are Polychloroprene-Neoprene, Butyl Rubber, Nitrile Rubber and Thiokol.
- Cannot be used for strongly oxidising conditions or halogenated carbon.
2) Plastic Lined Pipes :
- PTFE and PVC are most important lining materials.
- Used for chemical resistance, corossion protection,resist abrasion, non toxic and smooth bore reduces friction.
- PTFE is chemically inert and is used from -270 C to 260 C.
- PVC provide tough and heavy duty finish resistant to most acid and marine growth.















Comments
Post a Comment